In an era marked by climate extremes and rapid urbanization, resilient drainage infrastructure is no longer optional—it is a climate imperative. On June 5, 2025, the SIERA Academy convened another high-impact session in its Impact Series, spotlighting the urgent theme: “Building Resilient Drainage Systems for Climate Adaptation and Urban Sustainability.”
The webinar unpacked the rising threats posed by ineffective drainage in urban areas—from flash floods to pollution discharge—and laid out how forward-thinking planning, innovative solutions, and robust compliance frameworks can mitigate these risks. At the heart of the discussion was a dual focus: aligning with the European Sustainability Reporting Standards (ESRS) and leveraging circular water systems as both a sustainability and financial opportunity.
In this blog, we will explore the key insights from the webinar—from regulatory expectations and sustainability challenges to technical planning approaches and real-world solutions. With a focus on climate resilience, regulatory alignment, and urban infrastructure modernization, we’ll look at how effective drainage planning can unlock broader environmental and economic benefits.
Challenges – Building Resilient Drainage Systems
Despite increasing awareness of climate risks, many cities across Europe are still struggling to modernize their drainage infrastructure. Extreme weather events—particularly intense rainfall and flash flooding—are becoming more frequent, placing immense pressure on outdated or undersized drainage networks. In many urban areas, existing systems were never designed to cope with today’s climate realities.
One of the major challenges lies in the lack of climate-adapted infrastructure. Decades-old combined sewer systems are often overwhelmed during heavy precipitation, leading to urban flooding, water pollution, and costly damage. Moreover, impervious surfaces continue to grow with urban sprawl, reducing natural infiltration and increasing surface runoff.
Compounding this is the fragmentation of responsibilities. Drainage planning often involves multiple stakeholders—including city engineers, water utilities, environmental agencies, and private developers—making it difficult to coordinate integrated resilience strategies.
Additionally, limited digitalization and data access remain critical barriers. Many municipalities lack geospatial mapping of sewer networks, flood risk modeling, or up-to-date monitoring systems. Without this data, it’s challenging to assess vulnerability, prioritize investments, or comply with EU resilience planning standards.
Finally, financial and regulatory constraints delay infrastructure upgrades. High investment costs, complex funding mechanisms, and limited technical expertise—especially in smaller municipalities—hinder the timely adoption of resilient drainage solutions.
To break these systemic barriers, the webinar emphasized the need for forward-looking planning, interdepartmental coordination, and scalable, climate-resilient technologies tailored to local contexts.
Opportunities from Building Resilient Drainage Systems
Investing in resilient drainage systems is not just about mitigating environmental risks—it also unlocks tangible economic, regulatory, and reputational benefits. These systems, when designed with foresight and aligned with EU and ESG frameworks, offer value well beyond compliance.
| Opportunity | Explanation |
| 1. Access to Green Financing and ESG Investments | Resilient drainage systems align with EU Taxonomy and CSRD disclosure requirements, making companies eligible for green loans, grants, and sustainability-linked investments. This enhances investor confidence and lowers capital costs for infrastructure projects. |
| 2. Cost Savings from Water and Utility Management | Circular water systems reduce procurement and wastewater discharge fees. For water-intensive operations, this can slash utility costs by up to 50%, while enabling stormwater and greywater reuse offers quick return on investment. |
| 3. Boost in Property Value and Market Differentiation | Flood-resilient infrastructure improves real estate value. Projects meeting LEED or BREEAM standards qualify for premium pricing, reduce insurance risks, and are more attractive to buyers and tenants focused on climate resilience. |
| 4. Avoidance of Regulatory Penalties | Proper drainage helps meet EU Water Framework and Urban Wastewater Directive standards. This prevents penalties linked to untreated discharge and strengthens corporate ESG ratings and legal compliance. |
By viewing drainage not as a technical afterthought but as a strategic asset, municipalities and businesses can convert climate adaptation into long-term opportunity. These advantages create a strong business case for investment in stormwater infrastructure aligned with environmental and financial goals.
Regulatory Implications in the EU for Drainage Systems
Building resilient drainage systems isn’t just a technical priority—it’s a legal and regulatory obligation. Across the EU, multiple directives, strategies, and national-level laws are shaping how cities plan, operate, and finance drainage infrastructure in response to climate adaptation goals.
1. EU Adaptation Strategy and Climate Resilience
The European Union’s Climate Adaptation Strategy prioritizes infrastructure resilience across critical systems—including drainage and wastewater. Member States are expected to integrate adaptation considerations into urban planning, including stormwater management and flood risk mitigation.
2. EU Urban Wastewater Treatment Directive (UWWTD)
Currently under revision, the UWWTD sets out stricter standards for urban wastewater management. This includes improved treatment of stormwater overflows and combined sewer systems, placing pressure on cities to upgrade or separate drainage infrastructure.
3. EU Floods Directive
Under this directive, Member States are required to assess flood risks and implement flood risk management plans. These directly influence the design and retrofitting of drainage systems to reduce the impact of urban flash flooding.
4. National Climate Adaptation Laws
Countries like Germany have embedded drainage resilience in national frameworks. For example, municipalities are required to prepare adaptation concepts that include stormwater management and nature-based solutions. These legal mandates are increasingly linked to funding eligibility.
5. CSRD and ESG Reporting Standards
Under the Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD) and ESG standards, infrastructure-related disclosures—such as risks from flooding or drainage failures—must now be reported by large organizations. This creates additional pressure to adopt forward-looking planning and performance monitoring.
Solutions for Building Climate-Resilient Drainage Systems
As climate risks escalate and urban growth continues, the need for smarter, more adaptive drainage infrastructure becomes undeniable. During the SIERA Academy webinar, six integrated solutions were outlined—each addressing a critical aspect of resilient urban water management. From engineering design to digital governance, these strategies empower municipalities and private actors alike to align with EU sustainability directives while mitigating real-world risks.
1. Sustainable Urban Drainage System (SuDS) Assessments
SuDS are a cornerstone of modern, nature-based drainage solutions. They rely on ecological engineering principles such as permeable pavements, bio-swales, green roofs, and constructed wetlands to manage rainwater close to where it falls. These systems reduce stormwater runoff, filter pollutants, and allow groundwater recharge—all while enhancing local biodiversity.
In practice, SuDS assessments evaluate the feasibility of integrating features like retention ponds, filtration layers, and subsurface infiltration systems into urban landscapes. Combined with hydrological modelling, this approach optimizes infiltration and flow rates, directly reducing the burden on sewer systems and minimizing urban flood risks.
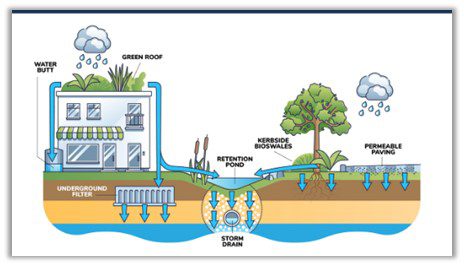
2. Circular Water Systems for Reuse in Drainage
Traditional drainage design often views stormwater as waste. In contrast, circular systems recognize it as a valuable resource. These solutions incorporate advanced water treatment technologies—including membrane filtration, UV disinfection, and biological treatment—to safely reuse stormwater and greywater.
Such systems allow for irrigation, industrial cooling, and even cleaning operations, drastically reducing water procurement costs. Smart storage tanks equipped with sensors enable real-time water level regulation and discharge optimization, enhancing water security in drought-prone regions and cutting utility costs by up to 50%.
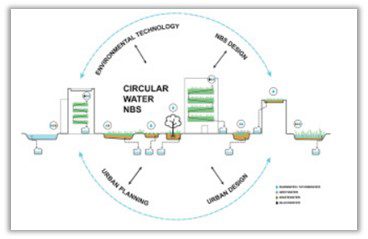
3. Integrated Drainage and Stormwater Management Planning
Engineering resilient cities requires integrated planning tools that simulate and forecast hydrological impacts. This solution leverages GIS-based spatial analysis and SWMM modelling to design drainage infrastructure that meets both current and future needs.
By optimizing pipe dimensions, slopes, and detention basin configurations, municipalities can enhance hydraulic performance and reduce flood exposure. The methodology also integrates urban growth projections and climate resilience parameters, ensuring long-term adaptability and alignment with sustainability goals.
4. Consultation on Pollution Control in Drainage Systems
Polluted stormwater runoff is a major source of environmental degradation and regulatory non-compliance. Effective control measures—such as oil-water separators, sedimentation tanks, grit chambers, and bio-filtration units—are essential for pollutant removal before water enters natural ecosystems.
This solution also involves expert guidance on continuous water quality monitoring, ensuring that systems meet EU Water Framework and Urban Wastewater Directive standards. By doing so, companies and municipalities can avoid penalties, safeguard aquatic habitats, and maintain positive ESG ratings.
5. SustainSuite – part of SIERA: Digital Support for Circular Economy Compliance
To make all these efforts measurable and compliant, SIERA offers SustainSuite, a purpose-built digital platform for circular economy governance. The software enables:
- Data-driven compliance: Automating alignment with EU Taxonomy, CSRD, and ESG frameworks.
- Impact tracking: Delivering real-time analytics to evaluate environmental and social metrics.
- ESG optimization: Enhancing sustainability outcomes through AI-powered reporting and smarter data collection.
By integrating SuDS assessments, circular reuse strategies, pollution control, and digital governance, these solutions provide a complete roadmap for building drainage systems that are not only climate-resilient—but also economically sound, environmentally restorative, and policy-aligned.
Case Study: Parkstadt Dösen Redevelopment – A Model of Decentralized Rainwater Management in Leipzig
A compelling example of how resilient drainage can be implemented at scale comes from Leipzig’s Parkstadt Dösen redevelopment project. The transformation of this 14.6-hectare former hospital complex into a sustainable residential area showcases how historical preservation, modern living, and climate resilience can be harmoniously integrated.
Urban Challenge and Sustainability Goals
The central challenge was to manage stormwater in an ecologically sound manner while protecting historic architecture and preserving valuable green spaces. With increasing pressure on drainage infrastructure due to climate change, the project embraced a forward-looking strategy: integrating natural water cycles into the urban landscape.
The development had to cope with a limited outlet capacity (Qmax ~434 l/s) and a downstream bottleneck at the Leinegraben bridge. To overcome this, a decentralized drainage approach was pursued—focused on infiltrating rainwater where possible and minimizing impervious surfaces.
Design and Technical Interventions
Across both the southern and northern parts of Parkstadt Dösen, the project implemented:
- 15 rainwater retention areas and 21 infiltration trenches
- Cisterns, storage channels (DN 1500), and green roofs
- Permeable pavements, drainage paving for parking areas
- Blue-green infrastructure above underground garages
- Wall greening, lawn combs for fire access, and retention throttling limited to 1 l/s
These measures were tailored to local soil conditions, which allowed for infiltration systems in the south but required retention and throttling in the north.
Climate Adaptation, Biodiversity, and Social Impact
The benefits of this integrated approach extended beyond water management. Tall trees and additional replanting created shading and cooling effects via evapotranspiration. The green and blue elements helped recharge groundwater, reduce surface runoff, and protect against flooding. Simultaneously, they enhanced biodiversity, improved the microclimate, and delivered a livable, green environment for future residents.
Results and Impact
The Parkstadt Dösen project demonstrates how decentralized, nature-based solutions can serve as a blueprint for climate-adaptive urban planning. It achieved:
- Sustainable drainage that relieves burdened sewer networks
- Compliance with heritage and environmental regulations
- A measurable reduction in flood risk and urban heat island effects
- Improved social and ecological quality of urban space
This case reinforces the broader message of the webinar: that resilient drainage is not just an engineering necessity but a pathway toward regenerative urban development.
Take the Next Step with SIERA
At SIERA Alliance, we equip municipalities, utilities, and infrastructure developers with actionable tools to design and implement climate-resilient drainage systems. In an era of intensifying rainfall and rising flood risk, we help turn vulnerability into opportunity—aligning engineering innovation with EU Green Deal objectives, CSRD compliance, and long-term urban sustainability.
Our integrated environmental engineering solutions ensure that resilient drainage planning is not only effective—but also economically viable, regulation-ready, and tailored to local conditions.
Our Services Include:
- Climate Risk & Hydraulic Load Analysis
We assess current and future hydrological pressures based on climate scenarios and regional precipitation trends to support resilient design decisions. - Smart Drainage Mapping & GIS Integration
Our teams use satellite, sensor, and spatial data to identify risk zones, simulate overflows, and optimize green-blue infrastructure layouts. - Nature-Based Solutions for Stormwater Retention
We integrate wetlands, rain gardens, swales, and pervious surfaces into urban infrastructure to maximize infiltration and minimize runoff. - SustainSuite – part of SIERA for Drainage Infrastructure
Our digital platform tracks drainage system performance, monitors emissions impact and helps document alignment with regulatory disclosures. We provide implementation strategies with clear milestones, supporting collaboration across public works, planning departments, and investors. Book a free demo now.
Get in touch with SIERA Alliance to learn how your city or region can benefit from intelligent drainage infrastructure. Whether you’re retrofitting legacy systems or planning climate-proof urban expansions, we help you deliver measurable resilience with every drop.
Engineering for a Better Tomorrow.








